Translate this page into:
Cryptococcal meningitis presenting as acute onset bilateral cerebellar infarct
Address for correspondence: Dr. Ajay Kumar Mishra, Department of Internal Medicine, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Vellore, Tamil Nadu, India. E-mail: ajaybalasore@gmail.com
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
This article was originally published by Medknow Publications & Media Pvt Ltd and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Sir,
A 59-year-old man without any previous vascular risk factors presented with 3-month duration of headache and gradual worsening of his sensorium. At the time of presentation, he had a low Glasgow coma scale (10/15) and neck stiffness; the remaining clinical examination was unremarkable. On initial evaluation, he was diagnosed to have HIV infection and his CD4 count was 43 cells/uL. His serum venereal disease research laboratory was nonreactive. His cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) examination showed lymphocytic pleocytosis (CSF white blood cell: 45/cumm, lymphocytes: 98%) and high protein (CSF protein: 1190 mg/dL, CSF glucose: 10 mg/dL). India ink of CSF was positive for cryptococci [Figure 1] and culture grew Cryptococcus neoformans [Figure 2]. Magnetic resonance imaging of his brain showed meningeal enhancement and evidence of acute bilateral cerebellar infarcts [Figure 3a–c]. Cryptococcal meningitis commonly presents as chronic meningitis in patients with impaired cellular immune response such as HIV.[1] One of the complications secondary to cryptococcal chronic meningitis is cerebral infarction. Cryptococcal meningitis presenting with stroke is rare, and most of these strokes are secondary to small vessel involvement.[2] Vascular involvement leading to cerebral infarction is secondary to direct toxic effect of the organism on vascular endothelium, antigen-antibody complex deposition causing vasculitis, strangulation of vessels passing through the basal exudates.[3] Previously infarcts in patients with cryptococcal meningitis have been reported to be in basal ganglia, internal capsule, and thalamus and these tend to be multiple.[24] Whether the presence of such infarcts is related to an adverse outcome is not yet known. Although our patient had bilateral infarcts, with the initiation of amphotericin therapy, he had optimal clinical improvement. This case highlights the uncommon spresentation of cryptococcal meningitis with bilateral cerebellar infarcts. As per author's knowledge, this is the first case report of acute onset bilateral cerebellar infarct in a patient with cryptococcal meningitis.
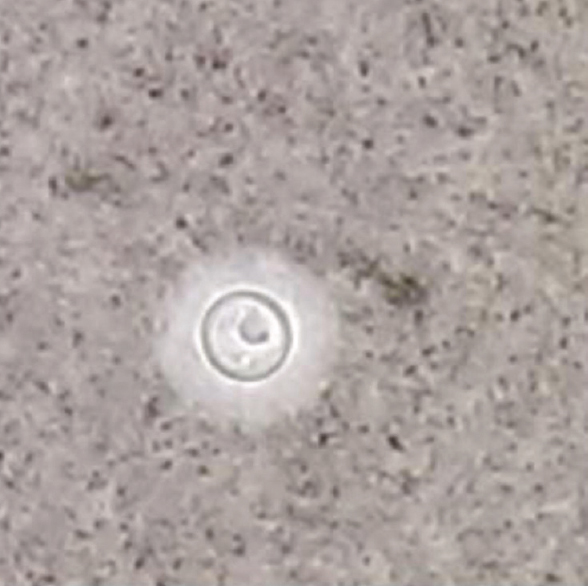

- India ink of cerebrospinal fluid ×400, clear halo around the organism denotes the presence of the capsule of Cryptococcus neoformans
- Sabouraud dextrose agar - mucoid, cream color colonies of Cryptococcus neoformans
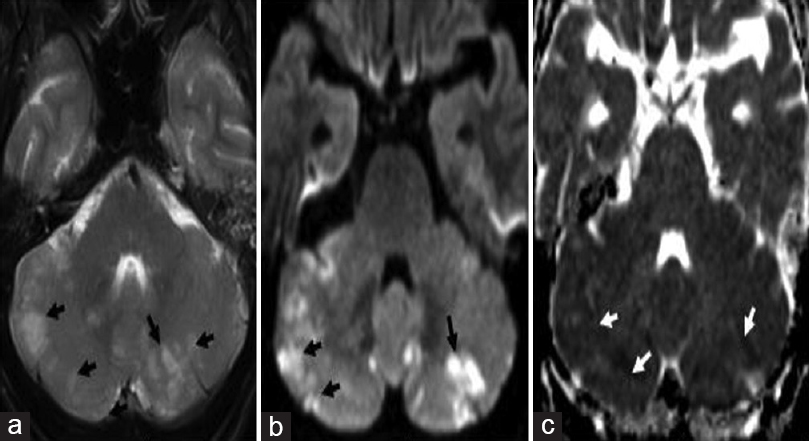
- Magnetic resonance imaging brain - arrows showing multiple hyperintense foci on T2-weighted images (a) in bilateral cerebellar hemispheres which have increased signal on diffusion-weighted images (b) and low signal on apparent diffusion coefficient images (c) suggestive of acute infarcts
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Changing paradigm of cryptococcal meningitis: an eight-year experience from a tertiary hospital in South India. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2015;33:25-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- Cerebral infarction in chronic meningitis: a comparison of tuberculous meningitis and cryptococcal meningitis. QJM. 2001;94:247-53.
- [Google Scholar]
- Sudden hemiparesis as the presenting sign in cryptococcal meningoencephalitis. Stroke. 1986;17:753-4.
- [Google Scholar]





