Translate this page into:
Sandwich Neurovascular Conflict of Optic Chiasm
Address for correspondence: Dr. Manchikanti Venkatesh, Department of Radiology, Narayana Medical College Hospital, Chinthareddypalem, Nellore - 524 003, Andhra Pradesh, India. E-mail: drvenkimdrd@rediffmail.com
This is an open access journal, and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
This article was originally published by Wolters Kluwer - Medknow and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
A 55-year-old female patient presented with a history of blurring of vision in both eyes (left > right). On visual field test, there was large central and peripheral visual field defect in the left eye [Figure 1a]. Rest of cranial nerves and neurological examination was normal. Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging with MR angiogram revealed increased signal intensity in the left half of the optic chiasm with tortuous loop of A1 segment of the right anterior cerebral artery (ACA) and supraclinoid left internal carotid artery (ICA) causing sandwich compression of the left half of optic chiasm [Figure 1b-d]. Visual loss due to dolichoectatic intracranial arteries and tumors were described in the literature. Elongated ACA rarely causes conflict with the optic pathway.[1] Vascular compression is usually seen with the 7th and 5th cranial nerves.[2] Our case is unique in which there is a sandwich compression of left optic chiasm by tortuous loop of contralateral ACA and ipsilateral ICA.
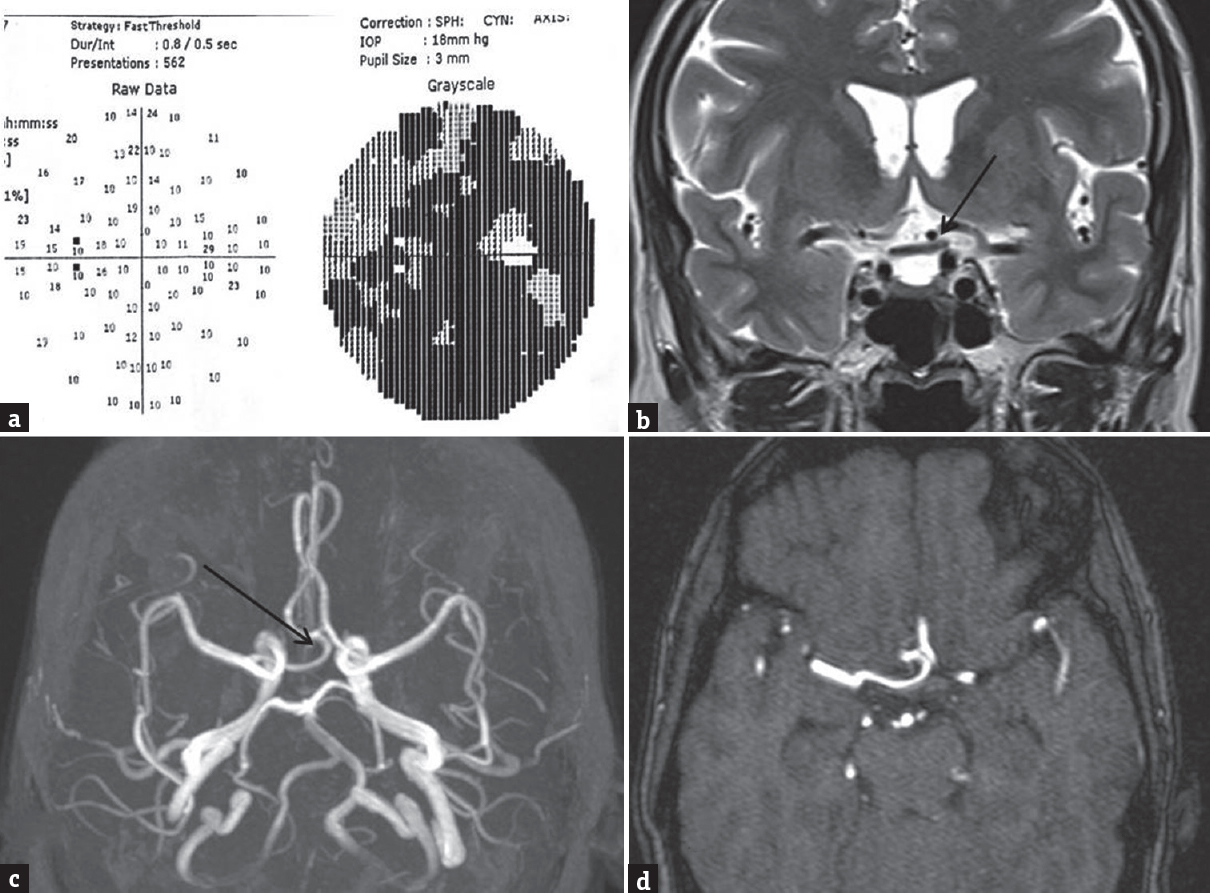
- (a-d) Perimetry and magnetic resonance images at the level of the optic chiasma and magnetic resonance angiogram shows large visual defect and tortuous A1 of right anterior cerebral artery compressing optic chiasm sandwiched by left supraclinoid part of internal carotid artery (arrow in b-d)
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms. In the form the patient(s) has/have given his/her/their consent for his/her/their images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal. The patients understand that their names and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal their identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- Microvascular decompression of the optic chiasm. Case report. J Neurosurg. 2011;114:857-60.
- [Google Scholar]
- Teaching neuroimages: Microvascular decompression of the optic nerve. Neurology. 2013;81:e137.
- [Google Scholar]





