Translate this page into:
Parietal Hand Weakness in a Patient with Astrocytoma
Chen Fei Ng, MD, MRCP Neurology Unit, Department of Medicine, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre Jalan Yaacob Latif, Bandar Tun Razak, 56000 Kuala Lumpur Malaysia n.chenfei@gmail.com
This article was originally published by Thieme Medical and Scientific Publishers Pvt. Ltd. and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
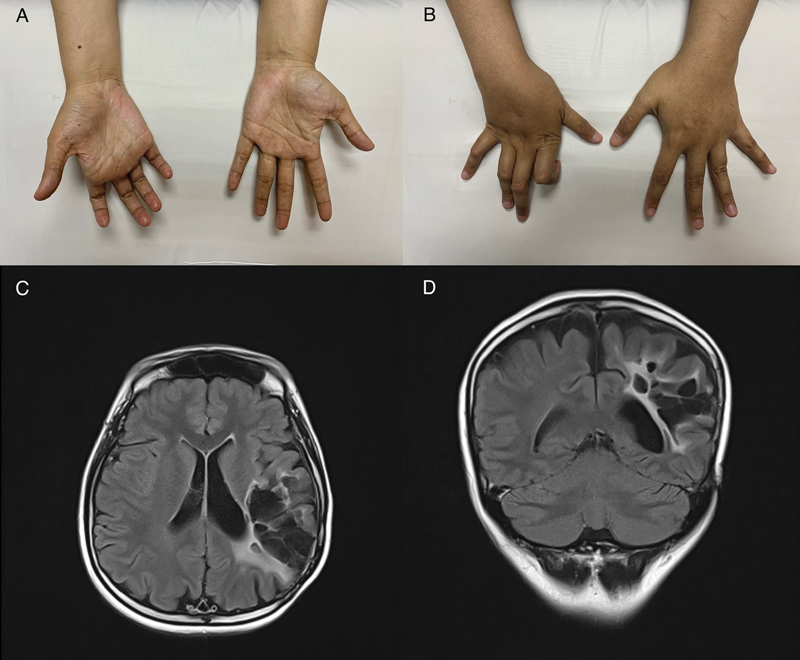
A 29-year-old woman was referred to neurology clinic for clawing of the right hand. She had a history of left parietal lobe astrocytoma 15 years ago for which she had surgical resection of the tumor and completed a course of chemotherapy and radiotherapy. She had since developed focal epilepsy and mild weakness of the right hand after the surgery. Examination of the upper limbs revealed distal hand weakness on the right side, with muscle power of ⅘ in the wrist and finger flexion and extension, ⅗ in the abductor digiti minimi, first dorsal interosseous, and abductor pollicis brevis. There were muscle wasting in the hypothenar muscles with clawing of the hand (Fig. 1A and B). The deep tendon reflexes of the right upper limb were brisk but there was no sensory deficit. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain revealed encephalomalacic changes in the left parietal region with no evidence of tumor recurrence. (Fig. 1C and D) Nerve conduction study of the upper limbs was normal and needle electromyography showed normal motor unit potentials with no neurogenic changes, apart from reduced central activation. The neurophysiology and neuroimaging findings lead to the diagnosis of parietal hand weakness.
-
Fig. 1 (A and B) Fingers clawing of the right hand with flexion of interphalangeal joints and hyperextension of metacarpophalangeal joints. (C and D) Cystic encephalomalacic changes in the left parietal region with ex-vacuo dilatation of the ipsilateral ventricle on fluid-attenuated inversion recovery sequence of magnetic resonance imaging brain.
Fig. 1 (A and B) Fingers clawing of the right hand with flexion of interphalangeal joints and hyperextension of metacarpophalangeal joints. (C and D) Cystic encephalomalacic changes in the left parietal region with ex-vacuo dilatation of the ipsilateral ventricle on fluid-attenuated inversion recovery sequence of magnetic resonance imaging brain.
The central cause of isolated hand palsy has been well recognized. The initial presentation of hand weakness and clawing may mimic a peripheral lesion such as ulnar palsy or brachial plexopathy. Celebisoy et al described eight patients with isolated hand palsy in acute cerebral infarction with discrete lesions confined to precentral gyrus.1 The term “cortical hand syndrome” has since been coined for the involvement of the specific motor hand area. On the contrary, isolated hand weakness is rarely seen in parietal lobe syndrome. Parietal lobe is primarily the cortical area for somatic sensations. However, parietal lobe lesions have also been associated with motor disorders in animals and humans. Some regions of the parietal cortex were thought to be involved in motor organization.2 The nonpyramidal weakness seen in parietal lobe pathology suggested that part of the parietal lobe contains somatotopic representation of the hand.
The diagnosis of parietal hand weakness is challenging as it may present as a pseudoperipheral nerve palsy. Neurophysiology investigation is very useful in ruling out neuropathy. It is essential for clinicians to recognize this entity to avoid missing a central pathology.
Conflict of Interest
None declared.
Funding None.
Reference
- Isolated hand palsy due to cortical infarction: localization of the motor hand area. Neurologist. 2007;13(6):376-379.
- [Google Scholar]
- Evolving isolated hand palsy: a parietal lobe syndrome associated with carotid artery disease. Brain. 1997;120:2251-2257. (Pt 12):
- [Google Scholar]






