Translate this page into:
All-trans-retinoic acid–induced pseudotumor cerebri in acute promyelocytic leukemia
Address for correspondence: Dr. T. M. Anoop, Department of Medical Oncology, Regional Cancer Centre, Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala - 695 011, India. E-mail: dranooptm@yahoo.co.in
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This article was originally published by Medknow Publications & Media Pvt Ltd and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Abstract
All-trans-retinoic acid is an integral part in the treatment strategy of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). Here we describe a case of pseudotumor cerebri associated with all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) during the induction therapy in an adult with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL).
Keywords
Pseudotumor cerebri
acute promyelocytic leukemia
all-trans retinoic acid
Introduction
Pseudotumor cerebri (PTC) or Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) is a disorder of elevated intracranial pressure (ICP) without any evidence of infection, vascular abnormality, space occupying lesion, hydrocephalus or alteration of consciousness.[1] All-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) has been widely used in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL).[2]
Cases of pseudotumor cerebri associated with all-trans-retinoic acid treatment in acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) have been frequently described in pediatric patients.[3] But it is rare in adults.
Case Report
A 25-year-old female patient presented to our clinic with fever and bleeding gums of three weeks duration. The clinical examination was normal except for a body temperature of 38.5°C. Systemic examination revealed no abnormality.
Hematological investigations showed hemoglobin of 10.7 g/dl, platelet count 200000/mm3; white blood cell count of 2900/mm3, differential count 30% blast cells, 6% neutrophils, 64% lymphocytes. Coagulation profile was normal. D-dimer was 10000 ng/ml. Serum biochemistry showed lactate dehydrogenase 566 U/L, peripheral smear showed normocytic normochromic anemia, reduced total count with predominant lymphocytes with atypical cells and adequate platelet count. Bone marrow examination showed 84% blasts which were peroxidase positive with moderate cytoplasm indented to bilobed nuclei with immature chromatin. Flow cytometry was suggestive of acute myeloid leukemia – M3 with CD13, CD33, CD64, CD117, CD45 positivity and negative HLA DR. Real time PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) qualitative analysis revealed the presence of typical fusion transcript PML-RARa (bcr1type) in the cells. Chromosomal analysis carried out using bone marrow showed 50% with 46XX; t (15;17) and 50% with 46XX. Detection of translocation t (15;17) by FISH using bone marrow showed PML-RARA fusion signal in 90% of interphase cells.
The patient was started on treatment with ATRA 45 mg/m2 p.o. (80 mg/day) plus daunorubicin 100 mg/day for four days. After three weeks of induction chemotherapy, the patient started complaining of headache and diplopia. Neurological examination was non contributory. Fundus examination showed bilateral papilledema. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain was normal. Cerebro spinal fluid (CSF) analysis was normal except for an elevated CSF pressure. Thus a diagnosis of PTC was made. ATRA was stopped and the patient was started on anti cerebral edema measures and steroids. Headache and diplopia subsided in two weeks. ATRA was restarted after one week. The patient achieved complete remission (CR) after induction chemotherapy without any neurological sequela.
Discussion
All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) is used as differentiation therapy for acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). Even though, ATRA is a well tolerated drug, some patients may develop complications like dry skin, retinoic acid syndrome, hypertriglyceridemia, sweet's syndrome, hyperleukocytosis, and rarely myositis.[456] The pathogenesis of ATRA-induced PTC is less understood. The mechanism of neurotoxicity is thought to be similar to the pathogenesis of hypervitaminosis A. At higher doses of ATRA, retinoids enhances the production of CSF and alters the lipid constituents of arachnoid villi, disrupting the normal transport system and impending the absorption of CSF at arachnoid villi. Warner et al. reported that CSF retinol levels were higher in patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) than in the subjects without IIH.[7] A progressive age-related reduction of RAR expression in the central nervous system has also been postulated as a reason for less chance of PTC in the adult APL compare to the children.[8]
Even though hallmark of PTC or IIH is papilledema, it can also occur in the absence of papilledema. MR imaging of the optic nerves and pituitary gland may provide important clues like flattening of the posterior sclera, vertical tortuosity and elongation of the optic nerve, distension of the perioptic subarachnoid space, compressed pituitary gland or empty sella.[917]
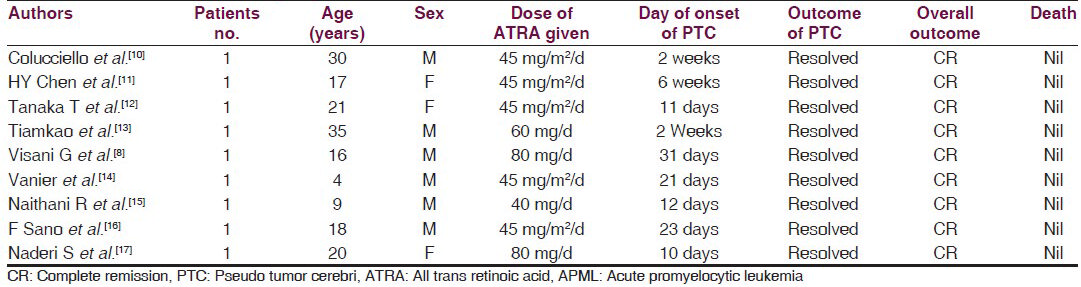
Table 1 shows the details of previously reported cases of PTC after ATRA for APML in the literature. Most cases were reported during the early 2-3 weeks of initiation of ATRA. Mortality was seen in none of the cases. There was no neurological sequela. This case highlights the possibility of pseudotumor cerebri while on therapy with ATRA even in the adult APML. A strong clinical judgment is necessary to stop ATRA at the onset of neurotoxicity and reinstitute ATRA at the right time to attain clinical remission.
Source of Support: Nil.
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
References
- Diagnostic criteria for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurology. 2002;59:1492-5.
- [Google Scholar]
- All-trans-retinoic acid as adifferentiating agent in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 1995;85:2643-53.
- [Google Scholar]
- Tretinoin toxicity in children with acute promyelocytic leukaemia. Lancet. 1993;342:1394-5.
- [Google Scholar]
- Rare but important adverse effects of all-trans retinoic acid in acute promyelocytic leukemia and their management. Int J Hematol. 1997;66:13-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- All-Trans-Retinoic acid-induced myositis in a child with acute promyelocytic leukemia. Haematologica. 2006;91:e97-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- Vitamin A in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with and without idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Ann Neurol. 2002;52:647-50.
- [Google Scholar]
- All-trans-retinoic acid and pseudotumor cerebri in a young adult with acute promyelocytic leukemia: A possible disease association. Haematologica. 1996;81:152-4.
- [Google Scholar]
- MR imaging of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001;22:196-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- Pseudotumor cerebri induced by all-trans retinoic acid treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Arch Ophthalmol. 2003;121:1064-5.
- [Google Scholar]
- ATRA-induced pseudotumour cerebri-one case report. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 1998;14:58-60.
- [Google Scholar]
- Intracranial hypertension in a patient with acute promyelocytic leukemia treated with all-trans retinoic acid. Rinsho Ketsueki. 1997;38:47-51.
- [Google Scholar]
- Pseudotumor cerebri caused by all-trans-retinoic acid: A case report. J Med Assoc Thai. 2000;83:1420-3.
- [Google Scholar]
- Interaction of all-trans-retinoic acid with fluconazole in acute promyelocytic leukemia. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2003;25:403-4.
- [Google Scholar]
- Pseudotumor cerebri in a child in early phase of induction therapy for APL with ATRA. Indian J Pediatr. 2009;76:439-40.
- [Google Scholar]
- Pseudotumor cerebri in a patient with acute promyelocytic leukemia during treatment with all-trans retinoic acid. Intern Med. 1998;37:546-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- Pseudotumour cerebri in acute promyelocytic leukemia: Improvement despite continued ATRA therapy. Ann Hematol. 1999;78:333-4.
- [Google Scholar]






