Translate this page into:
Aggressive Vertebral Hemangioma Causing Acute Spinal Cord Compression
Sokol Trungu, MD Via Pio X 4 Tricase, Italy s_trungu@hotmail.com
This article was originally published by Thieme Medical and Scientific Publishers and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
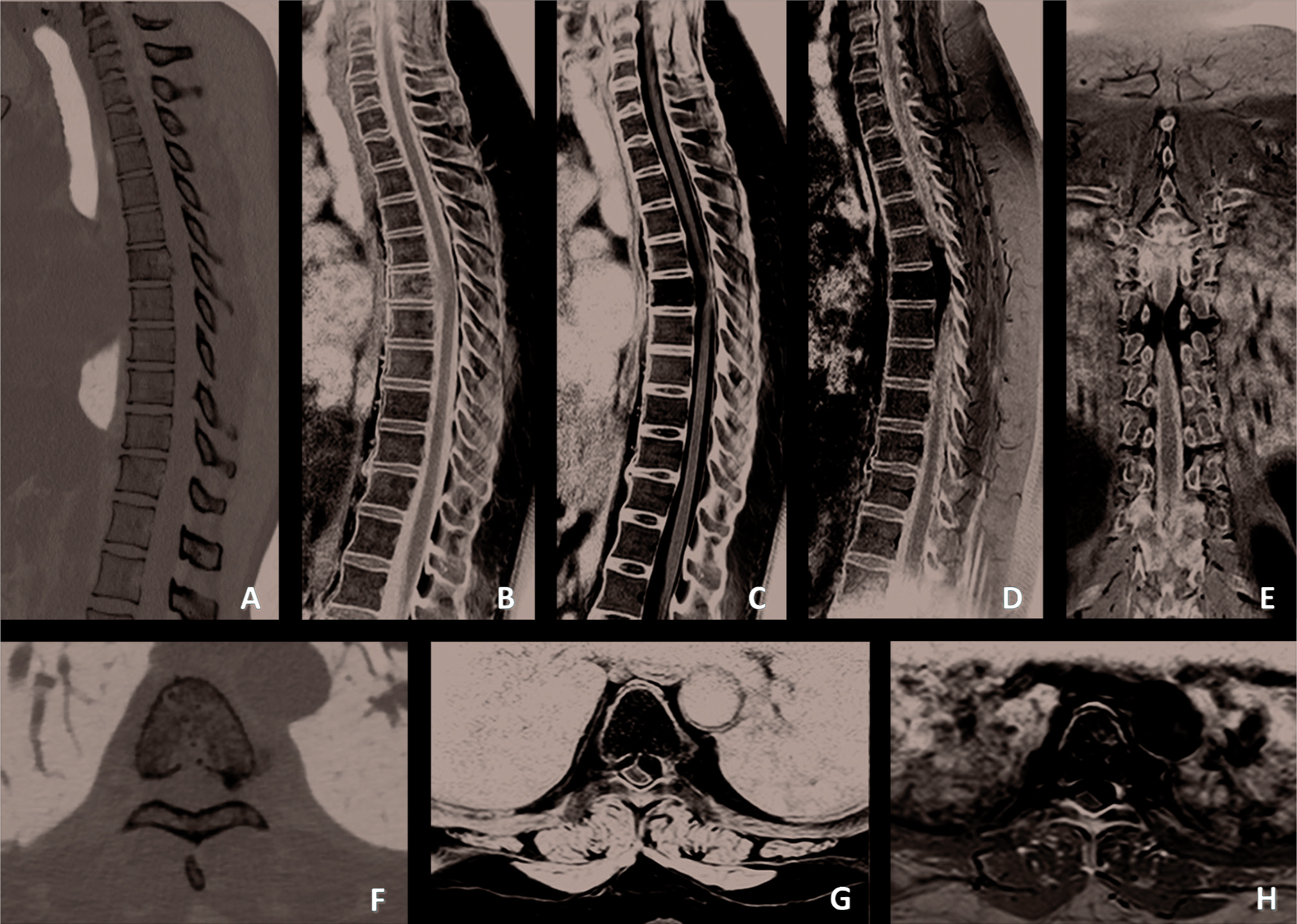
A 46-year-old woman presented to our emergency department with sudden onset of lower extremity weakness after physical activity. She referred only dorsal back pain before these symptoms. Neurologic examination revealed weakness 2/5 of lower limbs, hyperreflexia of deep tendon reflex of lower limbs, hypoesthesia under D7 level, and no sphincteric dysfunction. A computed tomography scan showed an accentuation of trabecular markings within the vertebral body and areas of lysis (Figs. 1A F). Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance images show diffuse abnormal marrow signal throughout the T6 vertebral body with epidural components with spinal cord compression (Fig. 1B H).
-
Fig. 1 Sagittal (A) and axial (F) computed tomography images demonstrating accentuation of trabecular markings within the vertebral body and areas of lysis involving the entire T6 vertebral body. Sagittal T1-weighted (B); sagittal (C) and axial (G) T2-weighted; sagittal (D), coronal (E), and axial (H) contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance images showing a T6 aggressive hemangioma with epidural extension and severe anterior cord compression.
Fig. 1 Sagittal (A) and axial (F) computed tomography images demonstrating accentuation of trabecular markings within the vertebral body and areas of lysis involving the entire T6 vertebral body. Sagittal T1-weighted (B); sagittal (C) and axial (G) T2-weighted; sagittal (D), coronal (E), and axial (H) contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance images showing a T6 aggressive hemangioma with epidural extension and severe anterior cord compression.
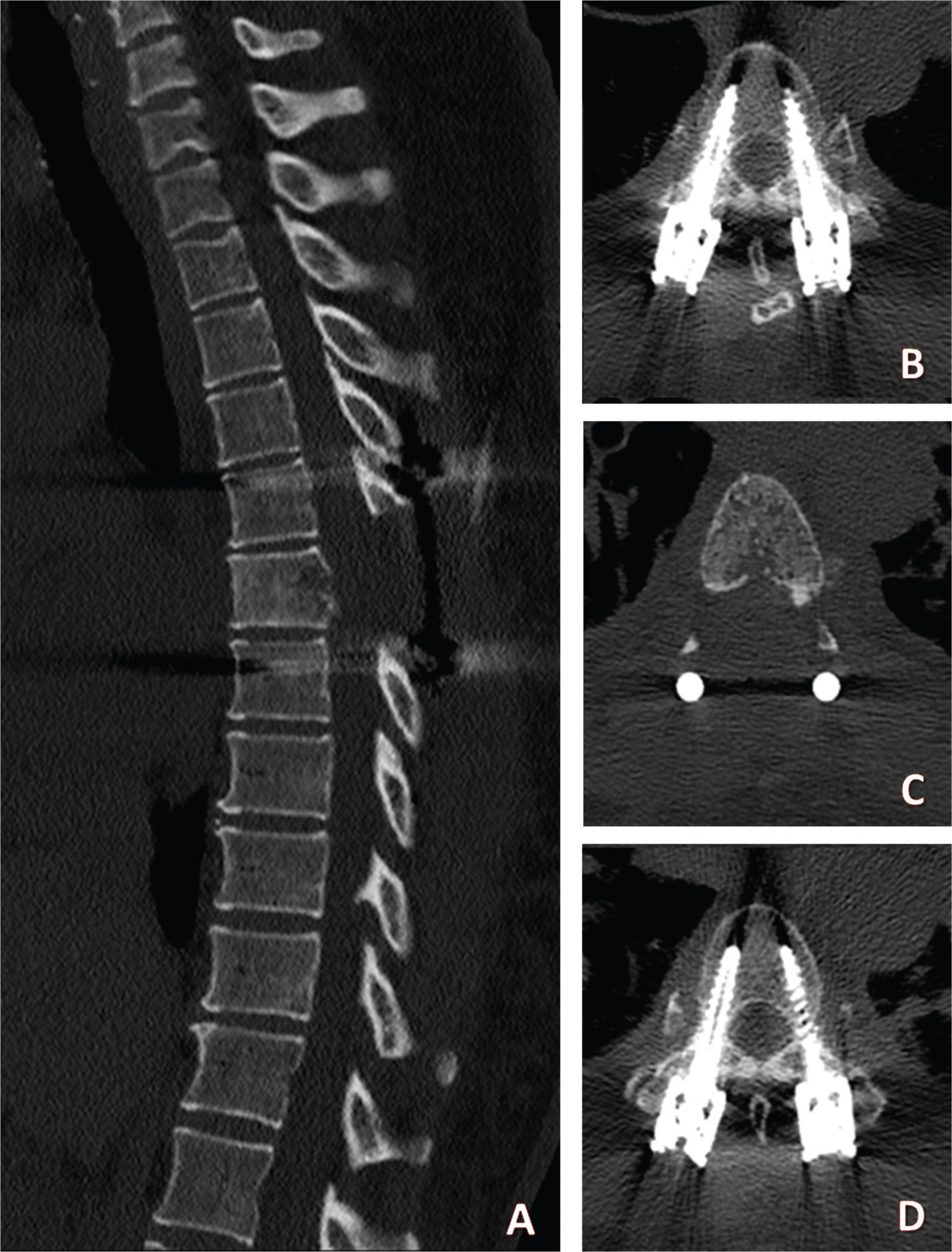
She underwent surgery on the same day through a mini-open decompression and percutaneous short posterior fixation (Fig. 2). No complications occurred after surgery with full recovery of neurological symptoms. Radiotherapy was perfomed after 4 weeks with resolution of dorsal back pain.
-
Fig. 2 Sagittal (A) and axial (B-D) postoperative computed tomography images demonstrating the posterior decompression and short pedicle screw fixation.
Fig. 2 Sagittal (A) and axial (B-D) postoperative computed tomography images demonstrating the posterior decompression and short pedicle screw fixation.
Vertebral hemangiomas (VH) are benign and generally asymptomatic primary vascular tumors of bone.1 2 Rarely, these lesions can cause symptoms due to cord compression as a result of bone expansion, erosion through cortex, fracture, or hematoma.3 Despite our long-standing recognition of aggressive VH, there is still a controversy regarding the optimal treatment strategy, and numerous therapeutic options have been described: embolization, surgery, radiotherapy, vertebroplasty, or a combination of them.4 5 6 7 8 9
Conflict of Interest
None declared.
Funding None.
References
- Symptomatic vertebral hemangiomas: MR findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996;167(2):359-364.
- [Google Scholar]
- Spinal hemangiomas: results of surgical management for local recurrence and mortality in a multicenter study. Spine. 2015;40(9):656-664.
- [Google Scholar]
- Vertebroplasty as treatment of aggressive and symptomatic vertebral hemangiomas: up to 4 years of follow-up. Neuroradiology. 2009;51(7):471-476.
- [Google Scholar]
- Diagnosis and treatment of vertebral hemangiomas with neurologic deficit: a report of 29 cases and literature review. Spine J. 2014;14(6):944-954.
- [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and imaging findings in patients with aggressive spinal hemangioma requiring surgical treatment. J Clin Neurosci. 2011;18(2):209-212.
- [Google Scholar]
- Vertebral hemangiomas with cord compression: the role of embolization in five cases. Surg Neurol. 1990;34(3):164-168.
- [Google Scholar]
- Transarterial embolization of vertebral hemangioma. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 1993;4(5):681-685.
- [Google Scholar]
- German Cooperative Group on Radiotherapy for Benign Diseases. Radiotherapy for symptomatic vertebral hemangiomas: results of a multicenter study and literature review. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;77(1):217-225.
- [Google Scholar]





