Translate this page into:
Neurocysticercosis presenting as pseudobulbar palsy
Address for correspondence: Dr. A.S. Praveen Kumar, Department of Medicine, PES Institute of Medical Science and Research, Kuppam - 517 425, Chittor, Andhra Pradesh, India. E-mail: jipmer.praveen@gmail.com
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This article was originally published by Medknow Publications & Media Pvt Ltd and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Abstract
Neurocysticercosis (NCC) is the most common helminthic infestation of the central nervous system (CNS) and a leading cause of acquired epilepsy worldwide. The common manifestations of NCC are seizures and headache. The NCC as a cause of pseudobulbar palsy is very unusual and not reported yet in the literature. A pseudobulbar palsy can occur in any disorder that causes bilateral corticobulbar disease. The common etiologies of pseudobulbar palsy are vascular, demyelinative, or motor neuron disease. We report a 38-year-old female patient who presented with partial seizures and pseudobulbar palsy. The MRI brain showed multiple small cysts with scolex in both the cerebral hemispheres and a giant intraparenchymal cyst. Our patient responded well to standard treatment of neurocysticercosis and antiepileptics.
Keywords
Epilepsy
neurocysticercosis
pseudobulbar palsy
taenia solium
Introduction
Neurocysticercosis (NCC) is the most common parasitic disease of the central nervous system (CNS) caused by the larval stage of the tapeworm Taenia solium and is the single most common cause of acquired epileptic seizures in the world.[1] It results from ingestion of the eggs of Taenia solium. Giant intraparenchymal NCC is a rare condition defined by various authors as measuring more than 4 or 5 cm in its largest dimension.[2] Clinical manifestations of NCC are nonspecific and varied according to the location, number and size of cysts, and host immune response to the cysticerci.[3] The most common manifestation is seizures, occurring in 50% to 80% of the patients. The occurrence of pseudobulbar palsy in NCC is not reported yet in the literature as per our knowledge. We report a case of diffuse intraparenchymal NCC involving both the cerebral hemispheres with pseudobulbar palsy and seizures.
Case Report
A 38-year-old female patient presented with progressive dysarthria, dysphagia, nasal regurgitation and hyper nasal speech for 5 months duration. She had 4 episodes of partial seizures involving the right upper and the lower limb for the past 5 months and was not on any medications. There was weakness of the left upper limb for the past 15 days duration but there was no headache, vomiting or blurring of vision. She had emotional instability in the form of inappropriate crying. Neurological examination showed exaggerated jaw jerks and gag reflex with spastic dysarthria. She had both proximal and distal weakness in the left upper limb with power of 3/5. All the deep tendon reflexes were brisk with plantar response mute bilaterally and cortical sensory loss in the left upper limb. There was no atrophy or fasciculation of the affected muscles. The fundus and other system examination were normal.
Laboratory examination revealed positive neurocysticercosis serology. The peripheral smear was normal. The renal and liver function tests were normal. The MRI brain showed multiple small cysts with scolex in both the cerebral hemispheres and a giant intraparenchymal cyst measuring 5 × 4.3 cms in the right cerebral hemisphere [Figure 1a and b].
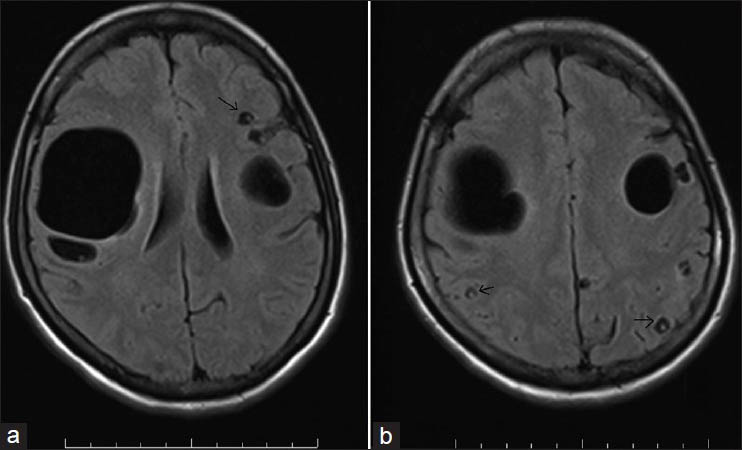
- MRI brain (T1W images) showing the giant intraparenchymal cyst (a) and multiple small cysts with scolex in vesicular stage (a and b, black arrows)
Our patient presented with pseudobulbar palsy, partial seizures and weakness of the left upper limb. Her NCC serology was positive and diagnosis confirmed by MRI, which showed multiple cysts with scolex (in vesicular stage). She received the treatment with albendazole at 15 mg/kg/day along with steroids (for two weeks). She also received phenytoin for seizures. The patient remained seizure free and there were no significant events during her hospital stay. On follow-up six weeks after the completion of albendazole therapy she reported no recurrence of seizures and her right upper limb weakness recovered partially with power of 4/5. There was also improvement in her speech, emotional instability and was able to take food without nasal regurgitation.
Discussion
Pseudo bulbar palsy is not a disease but clinical syndrome. The diseases that involve the corticobulbar tracts bilaterally result in pseudobulbar palsy (spastic bulbar palsy). It is characterized by dysphagia, dysphonia and anarthria or dysarthria often with paresis of the tongue and facial muscles.[4] The jaw jerk and other facial reflexes usually become exaggerated with retained or increased palatal reflexes. They have disordered emotional expression characterized by outbursts of involuntary, uncontrollable and stereotyped laughing or crying.[4] The disinhibition affective syndrome characterized by involuntary and inappropriate outbursts of laughter and/or crying is pseudobulbar affect (PBA). The common etiologies of pseudobulbar palsy are vascular, demyelinative, or motor neuron disease. The neurocysticercosis as a cause of pseudobulbar palsy is very unusual and no reports are yet in the literature as per our knowledge.
The usual presentation of parenchymal NCC is with seizures or headaches.[5] Occasionally the cysts may grow in size and produce a mass effect. Extraparenchymal infection may cause hydrocephalus by mechanical obstruction of the ventricles or the basal cisterns, either by the cysts themselves or by an inflammatory reaction (ependymitis and/or arachnoiditis). Cysticercotic arachnoiditis can lead to entrapment of cranial nerves (CN) in the inflammatory exudates that occur on the ventral aspect of the brain causing CN palsies. Extraocular muscle paralysis, diplopia and pupillary abnormalities can result from entrapment of the ocular motor nerves.[1] The cerebrovascular complications like cerebral infarction, transient ischemic attacks and brain hemorrhage can occur due do NCC.[6] The study by Cantu et al. showed angiographic evidence of cerebral arteritis in the patients with subarachnoid cysticercosis.[7]
The giant NCC usually occurs in the subarachnoid space. The intraparenchymal cysts rarely enlarge over 2 cms because the pressure of brain parenchyma limits the growth of cyst and hence giant intraparenchymal cysts are very rare.[8] The giant intraparenchymal NCC in addition to seizures can cause pressure effects due to compression of adjacent structures resulting in focal neurological signs and features of elevated intracranial hypertension. The diagnosis of NCC is mainly based on neuroimaging studies and antibody detection in the serum. Both computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are able to show the invaginated scolex but MRI is more sensitive than CT scan for the diagnosis.
In conclusion the diffuse intraparenchymal NCC should be included in the differential diagnosis of pseudobulbar palsy with seizures.
Source of Support: Nil.
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
References
- Results of surgical treatment of neurocysticercosis in 69 cases. J Neurosurg. 1986;65:309-15.
- [Google Scholar]
- Recent advances in the diagnosis and treatment of cerebral cysticercosis. N Engl J Med. 1984;311:1492-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- In disorders of Speech and language. In: Adams and Victor's Principles of Neurology (8th ed). New York: The McGraw-Hill Companies; 2005. p. :426.
- [Google Scholar]
- Frequency of cerebral arteritis in subarachnoid cysticercosis: An angiographic study. Stroke. 1998;29:123-5.
- [Google Scholar]






