Translate this page into:
Frontocallosal leucoencephalopathy in subacute sclerosing panencephalits
Address for correspondence: Dr. CJ Suresh Chandran, Department of Neurology, Kerala Institute of Medical Sciences, Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, India. E-mail: cjsureshchandran@gmail.com
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This article was originally published by Medknow Publications & Media Pvt Ltd and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
A 9-year-old girl presented with 3 months history of progressive cognitive decline and myoclonic jerks. She was not vaccinated for measles. Clinical examination revealed bilateral pyramidal signs and axial myoclonus with slow relaxation. Electroencephalogram showed characteristic long interval generalized periodic high amplitude sharp and slow waves [Figure 1]. Cerebrospinal fluid examination showed mild lymphocytic pleocytosis. Cerebrospinal fluid and serum antimeasles antibody titers were strongly positive, confirming the diagnosis of subacute sclerosing panencephalits (SSPE).
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) brain showed T2 and FLAIR hyperintensities involving bilateral frontal subcortical regions and genu of corpus callosum–fronto callosal leucoencephalopathy [Figures 2–4]. These lesions were isointense on T1 images and did not show diffusion restriction.
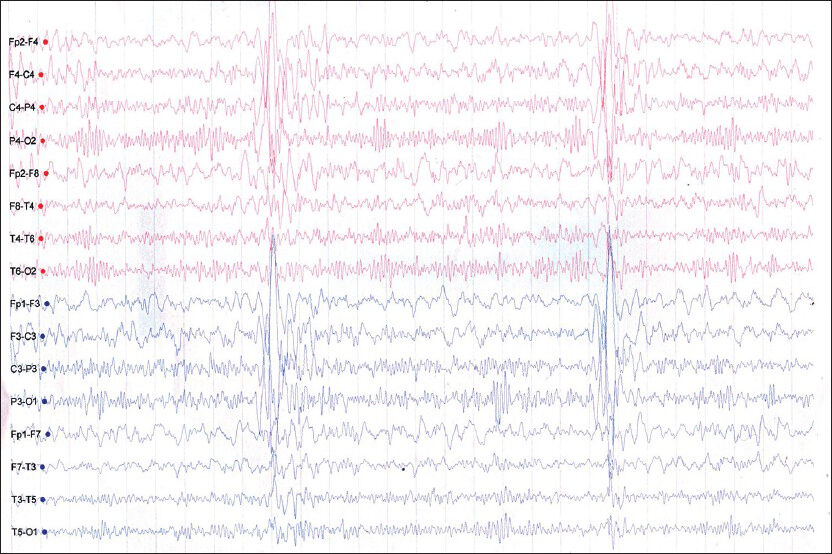
- Electroencephalogram showing generalized long interval periodic complexes
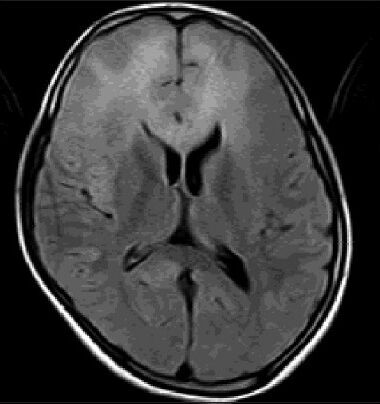
- Axial FLAIR image showing hyperintensities in bilateral frontal subcortical white matter and genu of corpus callosum
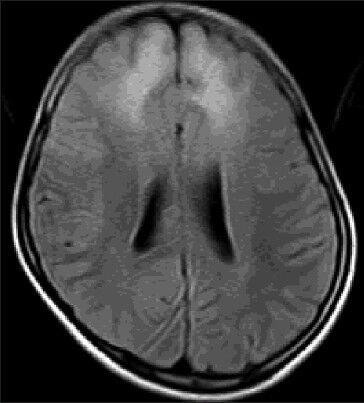
- Axial FLAIR image showing bilateral frontal subcortical white matter hyperintensities
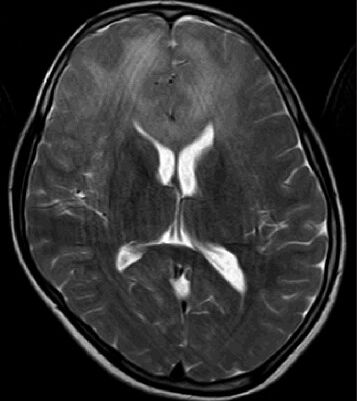
- Axial T2 image showing frontocallosal leucoencephalopathy
Discussion
SSPE is a slowly progressive fatal inflammatory disease of the central nervous system, developing as a sequel to childhood measles infection. SSPE is characterized by cognitive decline, stereotyped myoclonic jerks, generalized periodic complexes, and elevated CSF antimeasles antibody. The disease is clinically staged into four stages as per the modified Jabbour criteria: Stage I–cognitive decline and behavioral changes; Stage II–myoclonic jerks, choreo-athetosis, and gait disturbances; Stage III–decerebrate and decorticate posturing; Stage IV–bedridden, flexion posturing, and mutism. Our patient was in Stage II. The incidence of the disease is more in developing countries and males are affected more than females. Incidence varies from 0.04/million/year to 2.0/million/year. Incidence of SSPE has dramatically fallen over years due to immunization against measles. SSPE has a relentlessly progressive clinical course, resulting in death within 1-3 years after the diagnosis. Sodium valproate and clonazepam are useful for controlling myoclonus. A combination of oral isoprinosine and intraventricular alpha-interferon may influence the course of the disease.
Cranial MRI at initial diagnosis may be normal. Abnormal MRI findings are significantly more frequent in the later stages of the disease. So a normal initial cranial MRI does not exclude SSPE.[1] Periventricular or subcortical white matter T2-hyperintense lesions are the most common MRI finding in SSPE.[2] Lesions tend to start in the subcortical white matter and progress with periventricular white matter involvement and diffuse cerebral atrophy. The atrophic changes lag behind the white matter changes.[23] The lesions usually involve parietooccipital or parietotemporal cortico-subcortical regions asymmetrically.[24] Pial and parenchymal contrast enhancement, local mass effect of parenchymal lesions, involvement of the splenium of the corpus callosum, basal ganglia, and brainstem lesions are the other MRI findings reported in SSPE.[123] Frontal predominant white matter involvement in SSPE has been reported very rarely.[5]
Our case shows exclusive frontal subcortical white matter and genu of corpus callosum involvement without involvement of posterior regions. This frontocallosal leukoencephalopathy is a rare MRI finding in SSPE. MRI differential diagnosis of frontocallosal leukoencephalopathy includes gliomatosis cerebri, acute demyelinating encephalomyelitis, Alexander's disease, lymphoma, toxic leukoencephalopathy, and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. SSPE may be considered in the MRI differential diagnosis of anterior predominant leucoencephalopathies.
Source of Support: Nil.
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
References
- Epidemiological findings and clinical and magnetic resonance presentations in subacute sclerosing panencephalits. J Int Med Res. 2011;39:594-602.
- [Google Scholar]
- Subacute sclerosing panencephalits: Evaluation with CT and MR. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1996;17:761-72.
- [Google Scholar]
- Subacute sclerosing panencephalits: Clinical and magnetic resonance evaluation of 36 patients. J Child Neurol. 2002;17:25-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- A rare presentation of sub acute sclerosing panencephalits with acute fulminant course and atypical radiological features. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2013;16:732-3.
- [Google Scholar]





