Translate this page into:
Bilateral intracranial and spinal subdural hematoma presenting as bilateral sciatica
Address for correspondence: Dr. K. J. Jibu, Department of Neurology, PSG Institute of Medical Sciences and Research, Coimbatore, India. E-mail: drjibukjo@yahoo.com
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This article was originally published by Medknow Publications & Media Pvt Ltd and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Sir,
A 73-year-old man with no significant medical illness in the past presented to outpatient department with bilateral sciatic pain of 10 days duration. There was no history of postural headache or trauma. Neurologic examination showed normal fundus, visual acuity, motor power, and sensations in all four limbs. Deep tendon reflexes were normal in upper limbs and absent in lower limbs with flexor plantar response. Straight leg raising test was positive at 40 degrees bilaterally and low back tenderness was noted at L4, L5 level. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of spine showed spinal subdural hematoma (SDH) extending from L3 to S2 vertebral levels [Figure 1a]. While screening the brain, SDH was noted along the bilateral frontotemporoparietal convexities with maximum thickness of 1.5 cm [Figure 1b]. Hemogram, prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time, and inflammatory markers, including C-reactive protein were normal. The patient was managed conservatively and improved symptomatically over 2 weeks.
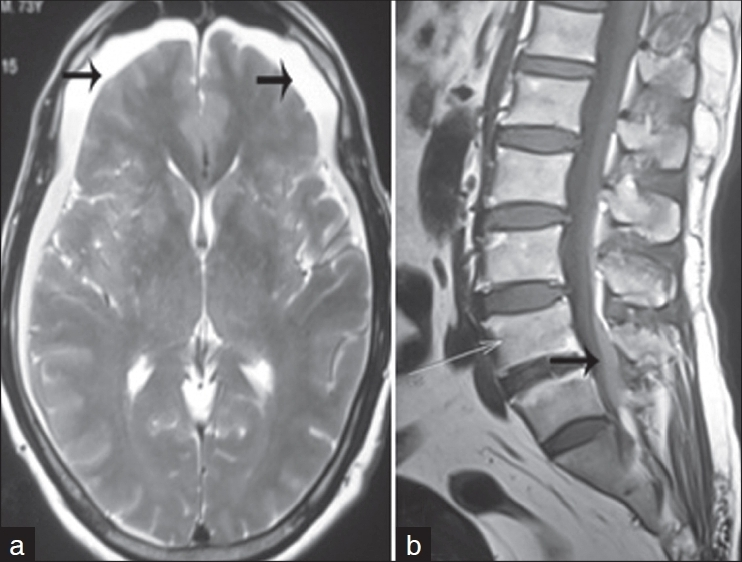
- (a) Axial T2-weighted brain image shows subdural hemorrhage along bilateral frontotemporoparietal convexities (black arrow); (b) sagittal T1-weighted spine image shows subdural hemorrhage along the posterior thecal sac extending from L3 to S2 vertebra (black arrow)
One month later, the patient again presented with confusion and mild left hemiparesis. Computed tomography brain showed bilateral large frontotemporoparietal subacute on chronic SDH about 2 cm in thickness on both sides, with midline shift of 4 mm [Figure 2]. Craniotomy was performed and hematoma was evacuated. The patient improved and follow-up MRI brain after 2 weeks showed significant resorption of hematoma and complete clearance of lumbar SDH [Figure 3a and b]. At 6 months follow-up, he had no recurrence of his symptoms.
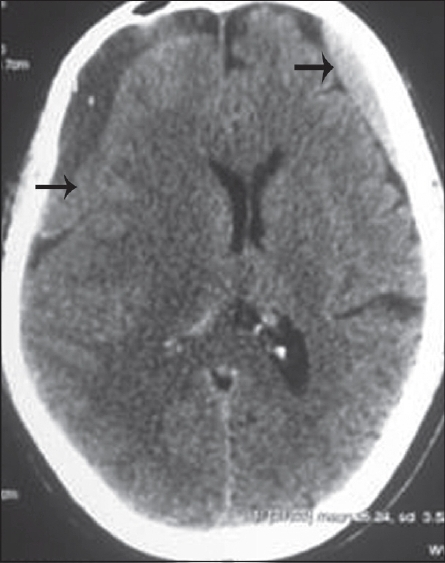
- Axial CT brain shows bilateral large frontotemporoparietal subacute on chronic subdural hemorrhage about 2 cm in thickness on both sides, with significant midline shift (black arrow)
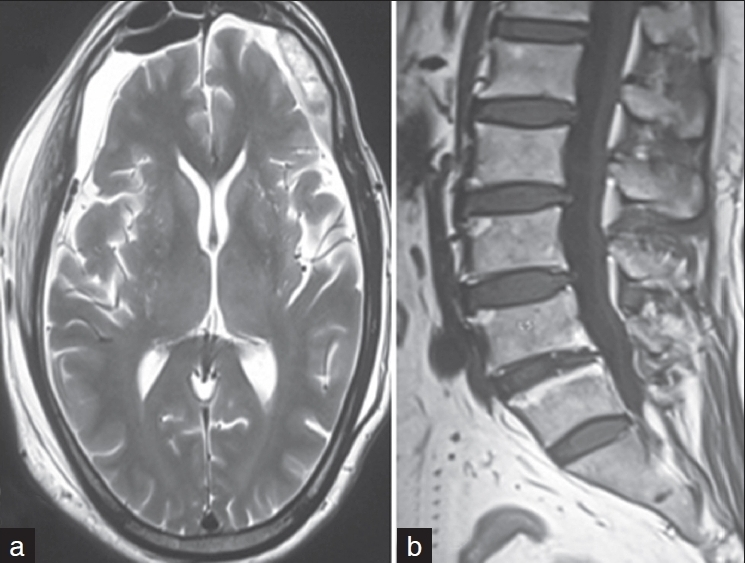
- (a) Axial T2-weighted brain image shows significant resorption of hematoma with no midline shift; (b) sagittal T1-weighted spine image shows complete resorption of hematoma
Spinal SDH is a rare entity, and its concomitant occurrence with cranial SDH is even extremely rare, in the literature.[1] The usual predisposing factors for spinal SDH include coagulopathies, lumbar punctures, trauma, and vascular malformation. In our patient, no evidence of vascular abnormality was found by MRI. There was also no evidence of bleeding or coagulation disorders. No previous history of lumbar puncture, surgery, or trauma could be obtained. Furthermore, the simultaneous appearance of intracranial and spinal SDH, suggested a close relationship between the SDHs. The etiology of simultaneous occurrence of spontaneous spinal and cranial SDH is obscure. Intracranial SDH can grow or redistribute as time progresses. Thus, the blood can distribute to the spinal subdural space, although this is rare, under the influence of gravity.[2] Lecouvet et al. explained that the propagation of blood from cranial to spinal subdural space is possible due to the presence of anatomic continuity between them.[3] Either low or high intracranial pressure has been proposed as a predisposing factor. The majority of the reported cases of concomitant cranial and spinal SDH showed good recovery on conservative management. Although the spinal SDH cleared spontaneously in our patient, there was intracranial subdural rebleed, requiring surgical evacuation. In the presence of a spontaneous spinal hematoma, MRI of the brain and the entire spine is essential for complete diagnosis and early prompt management.
References
- Spontaneous spinal and intracranial subdural hematoma. J Formos Med Assoc. 2009;108:258-61.
- [Google Scholar]
- Uncommon magnetic resonance imaging observation of lumbar subdural hematoma with cranial origin. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2003;27:530-3.
- [Google Scholar]





