Translate this page into:
Hyperammonemic Encephalopathy Associated with 5-Flurouracil Infusion in Head and Neck Cancer: Case Report and Review of the Literature
Saikat Das, MBBS, MTech, DMRT, MD, PhD, DNB, MNAMS Department of Radiotherapy, All India Institute of Medical Sciences Bhopal 462020, Madhya Pradesh India Saikat.radiotherapy@aiimsbhopal.edu.in
This article was originally published by Thieme Medical and Scientific Publishers Pvt. Ltd. and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Abstract
Abstract
Hyperammonemic encephalopathy is an uncommon, potentially lethal adverse effect of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU). Being one of the most common and versatile chemotherapy agents, it is important to understand this important side effect of 5FU. There is paucity of data in this subject. Here, we report a case of 5FU-induced encephalopathy in a patient on induction chemotherapy for head and neck cancer. In this case report, the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and management of 5FU-induced encephalopathy is reported.
Keywords
emergency neurology
oncology
pharmacokinetics
Introduction
5-flurouracil (5FU) is one of the most common anticancer drugs used in clinical oncology either alone or in combination with other systemic agents. 5FU-induced encephalopathy is a rare central nervous system (CNS) toxicity, which is characterized by altered neurological status with or without radiological and biochemical abnormality.1 Very few cases of 5FU-induced encephalopathy has been reported in the literature,2 and the reported annual incidence in Asian population is 0.1 to 1.1%.1 We report a very rare case of 5FU-induced acute neurotoxicity, characterized by confusion and ataxia in a patient undergoing 5FU-based induction chemotherapy for carcinoma of the buccal mucosa.
Case Report
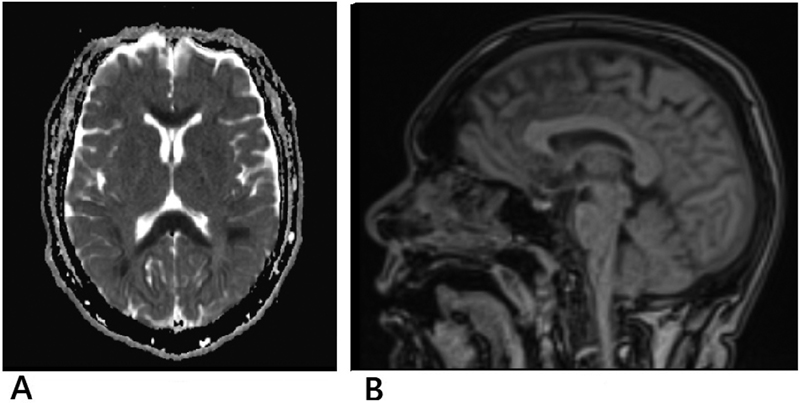
A 44-year-old man, diagnosed with carcinoma right buccal mucosa (stage: T4a N2b M0) with type 2 diabetes mellitus (managed on oral hypoglycemic drugs), was planned for induction chemotherapy with docetaxel, cisplatin and 5-day 5-FU. After the completion of the third day 5FU infusion in the first cycle of chemotherapy, he started experiencing vertigo and talking irrelevantly. There was transient episode of unresponsiveness to any command. Subsequently, he was agitated with altered sensorium. Serum electrolyte were within normal limits (serum Na—133, serum K—3.98 mg/dl). Serum phosphate level was mildly elevated (5.58 mg/dl). His arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis revealed respiratory alkalosis. Midazolam and haloperidol were used to calm him down during episodes of agitation. The patient was well-hydrated with normal saline infusion, and he improved after 12 hours, starting to respond to commands. Next day, he was again disoriented to time and place, and SpO2 level was 92%. He was put on oxygen at the rate of 4L/min, and SpO2 improved to 96%. In the afternoon, the patient again had an episode of blank stare, with rigidity affecting all the four limbs and unresponsive to painful stimuli. The diagnostic possibility of 5FU-induced acute encephalopathy was considered. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain revealed diffuse areas of hyperintensity in B/L centrum semiovale and subcortical areas and in the deep white matter along corpus callosum and B/L posterior limb of internal capsule, with corresponding drop in apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) mapping and possibility of acute toxic encephalopathy (Fig. 1). Blood ammonia level was elevated (66.4 µmol/L), indicating the possibility of hyperammonemic encephalopathy associated with 5FU infusion. He was started on injection valproate. Blood urea level was above normal limits (59.93 mg/dL), and serum creatinine level was 1.32 mg/dL. With intravenous hydration after 3 days, he was oriented to time, place and person, but with intermittent episodes of altered sensorium and disorientation, which were treated symptomatically. With supportive treatment, he gradually recovered, and biochemical parameters were normalized over another 3 days. After complete recovery from encephalopathy, he was planned for postoperative radiotherapy. No further symptoms or signs of neurotoxicity were noticed.
-
Fig. 1 Magnetic resonance imaging scan: (A) transverse section and (B) sagittal section showing diffuse areas of hyperintensity.
Fig. 1 Magnetic resonance imaging scan: (A) transverse section and (B) sagittal section showing diffuse areas of hyperintensity.
Discussion
Gastrointestinal and hematological toxicity are the main side effects of 5FU. Encephalopathy is a rare toxicity of 5FU infusion often associated with the high-dose continuous administration of 5FU.3 Although encephalopathy can present with broad spectrum of symptoms, ranging from mild to moderate (disorientation, altered sensorium), in some cases, it can be very severe, with clinical signs like generalized rigidity and seizure, leading to hepatorenal dysfunction and even death.1 The mechanism behind this neurotoxicity is not completely understood. It is postulated that accumulation of the by-products of 5-FU metabolism like fluoroacetate and fluorocitrate leads to metabolic derangement of citric acid cycle and urea cycle, causing accumulation of ammonia, which, in turn, leads to hyperammonemic neurotoxicity.4 Patients with genetic polymorphisms of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase enzyme (leading to dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency, DPD) or the TYMS gene are predisposed to 5FU-associated hyperammonemic encephalopathy due to the inability to detoxify the fluoropyrimidine derivatives in the liver.4 Pharmacokinetics of 5FU is also influenced by chronomodulation and circadian rhythm.5 This may be linked to the waxing and waning clinical presentation seen in our case.
Acute 5FU neurotoxicity is often reversible on discontinuation of the drug. The exclusion of intracranial metastases, carcinomatous meningitis, paraneoplastic syndrome and neurologic manifestations of other medications and coexisting diseases with CNS effects is imperative. Approximately 57% patients with 5FU encephalopathy require intensive care, and the morality rate of this condition is 17%.1 There is no consensus on the treatment of 5FU-induced hyperammonemic encephalopathy, but conservative supportive measures are important. Our patient recovered gradually over a few days after ceasing the infusion of 5FU, fluid supplement and lactulose. Some studies have reported that administration of branched-chain amino acid or thiamine (in patients with cerebellar ataxia) are useful, which was not required in this case, as the patient improved with supportive measures. The French national survey study1 has shown high chance of relapse of encephalopathy on rechallenge (57%). We planned for postoperative radiotherapy for our patient. Patient is free of any residual neurological toxicity to date.
Conclusion
Hyperammonemic encephalopathy is rare, and with early diagnosis and supportive measures, it is often reversible on withdrawal of the drug. The role of circadian rhythm and chronomodulation remains to be investigated.
Conflict of Interest
None declared.
Funding None.
References
- 5-Fluorouracil-induced hyperammonaemic encephalopathy: A French national survey. Eur J Cancer. 2020;129:32-40.
- [Google Scholar]
- Prevention of 5-fluorouracil-induced early severe toxicity by pre-therapeutic dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency screening: Assessment of a multiparametric approach. Semin Oncol. 2017;44(1):13-23.
- [Google Scholar]
- Chemotherapy related encephalopathy in a patient with Stage IV cervical carcinoma treated with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil: a case report. Cases J. 2009;2:8526.
- [Google Scholar]
- Genetic polymorphisms associated with 5-Fluorouracil-induced neurotoxicity. Chemotherapy. 2010;56(4):313-317.
- [Google Scholar]
- Chronomodulated versus fixed-infusion-rate delivery of ambulatory chemotherapy with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and folinic acid (leucovorin) in patients with colorectal cancer metastases: a randomized multi-institutional trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994;86(21):1608-1617.
- [Google Scholar]






