Translate this page into:
Aneurysmal bone cyst of the cranio-vertebral junction: Benign or malignant?
Address for correspondence: Dr. Pravin Salunke, PGIMER, Sector 12, Chandigarh – 160 012, India. E-mail: drrpravin_salunke@yahoo.co.uk
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This article was originally published by Medknow Publications & Media Pvt Ltd and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Sir,
Aneurysmal bone cyst (ABC) is an expansile lytic lesion of the bone, characterized by multiple blood filled cavities with expanded bone forming its perimeter and is usually seen in children and young adults.[12] ABC of the spine generally involves the lamina, pedicles and the spinous processes. It may extend to the vertebral body and facets occasionally. Total excision usually bears a good outcome.[2] The ABC at cranio-vertebral junction (CVJ) is rare, and its management is difficult as compared to ABC at other sites. The proximity of the cervico-medullary junction, vertebral artery and the instability following surgical excision makes the management difficult.[3–5]
14-year-old male was presented with neck pain, with restricted neck movements and dysphagia with right 9th - 12th cranial nerve involvement for 7 months and progressive spastic quadriparesis (Right half weaker than the left). Radiology revealed a bony lytic expansile lesion, involving the atlas and the occipital condyle on the right side and partly destroying the left lateral mass. It was involving the right lateral mass engulfing the vertebral artery and encroaching anteriorly, compressing the cord [Figure 1]. The plan was staged surgical excision. During the first surgery, the vertebral artery was transposed, and lesion seen posteriorly and involving the right C1 lateral mass and occipital condyle was excised (akin to extreme lateral transcondylar approach). Instrumentation was used to fuse occiput and C2 on right side (screws in occiput and C2 facet fixed with rod) [Figure 1]. The histopathology confirmed ABC. The plan was to excise the remaining lesion in the second stage. His neck pain, quadriparesis and dysphagia improved. He followed up 8 weeks later with recurrence of quadriparesis and respiratory distress. An MRI showed recurrence of lesion posteriorly and increase in the residual lesion on left side [Figure 1]. The recurrent lesion, compressing the cord and that on the left side, was excised with occiptio-axial instrumentation on the left side [Figure 1]. Also, 200 i.u. of calcitonin with methylprednisolone was injected in the lesion that could not be excised. Post-operatively, he had a transient improvement, but worsened after a week and required ventilator support. He finally succumbed to respiratory infection and septicemia.
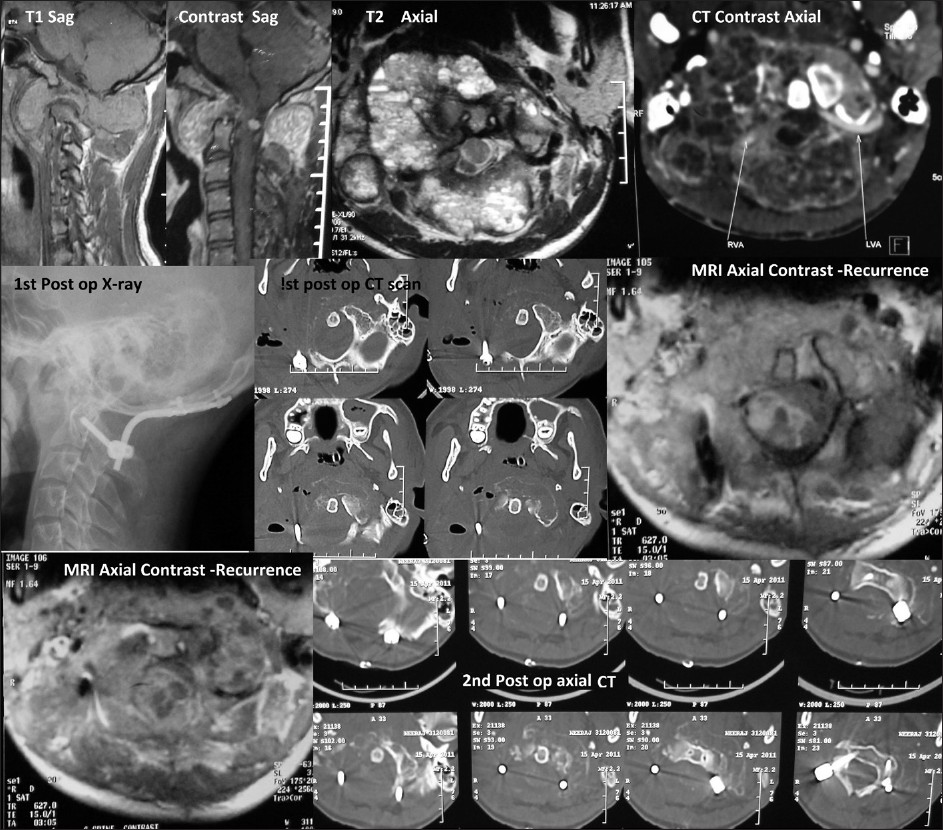
- Upper row- Preop images showing hypo-iso intense lesion (T1) showing extension across the facets with contrast enhancement. T2 axial image showing multiple cysts involving the posterior arch of atlas and extending into the right lateral mass, anterior arch and occipital condyle. Adjacent to that is pre-op CT showing expansile bony lesion and engulfed vertebral arteries (arrows). 2nd row. Post op CT and X-ray shows excision of lesion (right side) with instrumentation. Adjacent to that is MRI (axial) showing recurrence posteriorly followed by second postop CT scans showing instrumentation.
Presence of an expanded bone with multiple fluid levels (multiple cysts containing blood) clinches the diagnosis.[12] CT scan helps to determine the amount of bone involved. The neural structures compressed are defined by an MRI. Angiogram defines the course of vertebral artery. Besides, the feeding vessels can be embolized, if required.[5]
Total excision is desirable during surgery as the outcome following that is good.[2] However, total excision may not be achieved in a single stage in lesions, involving the cranio-vertebral junction. The vertebral artery needs to be protected, and as the facets are usually involved, stabilization needs to be planned preoperatively.
Another treatment option is injecting 200 i.u. intralesional calcitonin with 120 - 160 mg methylprednisolone, every 4 - 6 weeks for 4 to 6 times. This stimulates cyst ossification with new cancellous bone formation and reducing angiogenesis. However, it is useful only in patient without neurological deficits.[6] We tried to use this during the second surgery after decompression.
Superselective embolization using polyvinyl alcohol particles of arterial feeders has been occasionally used as a primary modality of treatment.[15] The main advantage is avoidance of radical surgery with rigid fixation. Embolizing arterial supply to adjacent normal tissue is the risk. In addition, multiple embolization procedures are necessary to achieve healing of the cyst as a consequence of multiple arterial feeders to a single cyst.[5]
Radiotherapy is usually used as an adjunct to surgery. However, it entails the danger of radiation induced myelopathy and deformity of the spine, especially in young patients.[2]
With partial excision, the recurrence rates are as high as 30%.[2] The recurrence may be as rapid as 6 - 8 weeks as occurred in our patient. This report highlights the aggressive behavior of such lesions when partially excised, and an importance of considering other treatment options early in the course, along with decompression in case total excision is not possible.
References
- Primary vertebral tumors: A review of epidemiologic, histological, and imaging findings, Part I: Benign tumors. Neurosurgery. 2011;69:1171-80.
- [Google Scholar]
- Aneurysmal bone cyst of spine: A review of literature. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008;128:1145-7.
- [Google Scholar]
- Aneurysmal bone cyst: Surgical management in the pediatric cervical spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34:E50-3.
- [Google Scholar]
- Aneurysmal bone cyst of the atlas: Successful treatment through selective arterial embolization: Case report. Neurosurgery. 2004;55:982.
- [Google Scholar]
- Aneurysmal bone cyst at C2: Imaging evaluation after intralesional injection of calcitonin andmethylprednisolone. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2008;66:711-5.
- [Google Scholar]





