Translate this page into:
Craniomapper: An accurate two-dimensional plane in localizing lesion during craniotomy
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
This article was originally published by Medknow Publications & Media Pvt Ltd and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Sir,
The precise localization of brain convexity lesions can be inaccurate due to the oval shape of the skull and also to unreliable external landmarks. Accuracy can be improved using intraoperative ultrasound, conventional and frameless stereotaxis and neuronavigation.[1234] Neuronavigation has become a standard procedure in many neurosurgical centers; however, in most departments worldwide, this tool is not available due to its high cost.
As long as computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are more accessible in hospitals or private institutions, good precision may be achieved by using these radiological tools to calculate the localization of brain convexity lesions beneath the skin. Unfortunately, not all the neurosurgical services can have such sophisticated and expensive intraoperative stereotactic systems.
We operated on 32 patients after localizing their lesion by using craniomapper. Twenty-one patients suffered from intracerebral hemorrhage, and the other 11 patients suffered from high convexity tumors.
A 30-year-old male presented by sudden onset of right side weakness and aphasia. On examination; the patient was fully conscious, oriented, and aphasic, with grade 1 right side hemiparesis. CT brain revealed left parietal intracerebral hematoma. He underwent CT scan again after putting craniomapper on his head. After getting the CT scans with craniomapper, the proper site for burr hole needed to evacuate the hematoma where precisely determine. The surgery where done using a single burr hole <1 cm in diameter and the hematoma where significantly evacuated through this tiny opening. Postoperatively, the patient recovered very well, and his hemiparesis was recovered completely over 1 month period. Immediate CT scans postoperatively revealed a significant reduction in hematoma which is nearly evacuated totally [Figure 1].
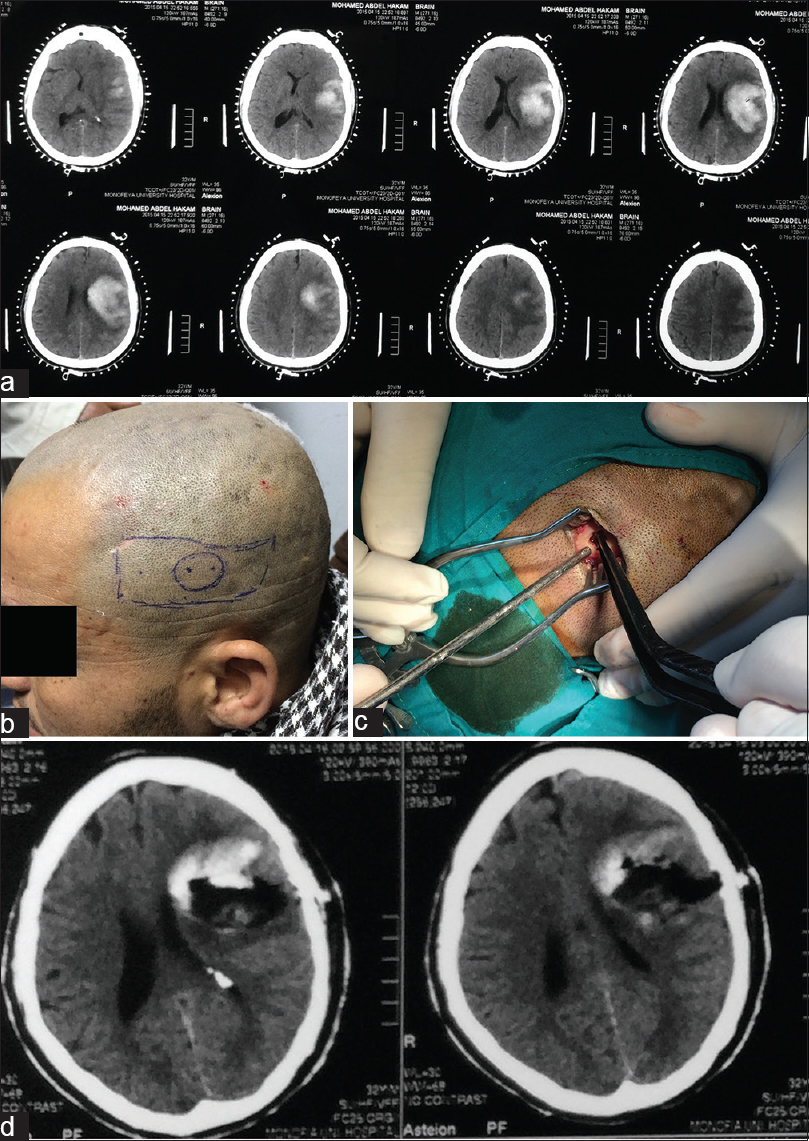
- (a) Computed tomography scans show large left mid and high parietal intracerebral hematoma with midline shift, (b) scalp markers on patient's head as rectangular mark is the hematoma, the circular mark is site proposed to be around the bur hole, and the two pints is the sites to place brain cannula, (c) the tinny burr hole used to evacuate hematoma, and (d) computed tomography scans show highly significantly evacuated large hematoma with subsequently resolved midline shift
A 46-year-old female patient presented by a sudden attack of convulsion before the time of admission. The convulsion was controlled by diazepam and phenytoin. On examination, the patient regained full consciousness postictal. She complained of right hemiparesis grade 3 which improved to grade 5 after dehydrating measures. CT scans and MRI with contrast revealed left parietal calcified space occupying lesion. She underwent CT scans again after putting craniomapper on her head and the proper site for craniotomy needed to remove the tumor where precisely determined using the craniomap CT scans. The surgery was done using an optimal craniotomy flap and the tumor was totally removed through this optimal opening. Postoperatively, the patient recovered very well. MRI postoperatively revealed total removal of the tumor [Figure 2].

- (a) Magnetic resonance T1-weighted images show left high parietal tumor, (b) computed tomography scans with superimposed craniomapper show the left high parietal tumor, (c) patient's photo shows scalp marks denoting the exact place of the tumor, and (d) postoperative magnetic resonance T1-weighted images with contrast show complete removal of the tumor
This craniomapper (Surgiwear, India) frame allows the surgeon to define precisely the two-dimensional planes for the targeted lesion in the brain and allow him/her to do operate the lesion with very small skull opening.
In all cases operated on, the margin of bony mistake “either for intracerebral hematomas or high convexity tumors” was almost totally vanished. Using the craniomapper as a new device for lesion localization proved to be very accurate either in the 21 patients who operated by a one cm diameter burr hole to evacuate intracerebral hematomas or in the 11 patients who treated for high convexity tumors by using very optimal craniotomy to totally remove the tumor. There were no lesional boundaries in all studied patients that need extra bony removal or more brain retraction.
Further, the use of a stereotactic frame or neuronavigation systems is not available widely in neurosurgical services in most of the low socioeconomic countries. The craniomapper can be an alternative in such neurosurgical centers when precise craniotomy is required for brain lesion in high convexity area. This is particularly can be applied in routine or emergency surgery where wide craniotomy is not desired. Furthermore, the craniomapper does not need any special training for the users and it is very safe for the patients.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Intraoperative localization using an armless, frameless stereotactic wand. Technical note. J Neurosurg. 1993;78:510-4.
- [Google Scholar]
- Near-real-time guidance using intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging for radical evacuation of hypertensive hematomas in the basal ganglia. Neurosurgery. 2000;47:1081-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- Johns Hopkins Medicine, Health Library. Craniotomy: Procedure Overview. Available from: http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/neurology_neurosurgery
- [Google Scholar]
- Frameless stereotactic neurosurgery using intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging: Stereotactic brain biopsy. Neurosurgery. 2000;47:1138-45.
- [Google Scholar]





